Polymer Processing : An Overview of various Plastic processing methods
The process of converting the plastic raw materials into semi-finishing or finished products is known as plastic processing or “Get the Shape and Set the Shape”.
Examples: Buckets, Mugs, Soap boxes, Crates, Tanks, Pipes, Shampoo bottles, Disposables, carry bags, Ropes, Bumpers, Profiles, etc.
Classification of Processing Methods
- Primary Processing Methods: Extent of utilization for Varied applications Growth Potential Ex: Injection Moulding, Extrusion, Blow Moulding, Compression / Transfer Moulding,
- Secondary Processing Methods: Lesser extent of utilisation Acts as supplementary to primary operation Ex: Roto Moulding, Thermoforming, Coating, Casting, FRP Fabrication Methods, Calendaring, etc.
Effect of Polymer Properties on Process Technique
- Water Absorption:
During processing of thermoplastic melts, the following factors should be taken into account in order to process efficiently and obtain quality products.
- Hygroscopic Materials
- Absorption phenomena – Ex: Nylon, POM and PC.
- Adsorption phenomena – Ex: HIPS, PS and ABS.
- All these materials should be pre-dried.
- Non-Hygroscopic material – Ex: PVC, Polyolefin, etc.
- Need not be predried. Except when completely wet during monsoon.
2. Physical Form of Raw Material –
- Powder form, granular form, lumpy/slab form
- Slab Form – Calendering, Compression Moulding
- Granular Form – Preferred – Uniform pellet size ensures even and faster feeding.
- Powder Form – Difficulty in feeding – But savings in cost because of the ability to avoid pelleting stage – Special feeder attachment essential to ensure proper feeding.
3. Thermal Stability of Polymers
- Higher melt temperature may leads to polymer degradation Eg. PMMA, POM upon depregation liberates MMA & formaldehyde respectively. MMA volatilizes and causes bubbles. Formaldehyde gas causes “eye-irritation”.
4. Adhesion of melt to metal:
- Wetting of the polymer melt against the metal wall of processing equipment can lead to strong adhesion of polymer to metal. Ex: difficulty in removing PVC mix from two roll mill.
- PC has a strong adhesion to metal. It can take away the skin of the barrel if not properly purged.
5. Thermal Properties Affecting Heating and Cooling
In the case of polymer melts, the specific heat varies with temperature. For crystalline polymers such as POM, NYLON etc. latent heat of fusion and specific heat should be taken into account. i.e Total heat content (Enthalpy) =LH of fusion + Sp. heat
6. Cooling Shrinkage and Compressibility
When polymers are in molten stage the vibrations of the molecules results in the polymer chain being pushed apart so that the volume occupied by a given polymer mass is higher than when the material is solid
The various processing techniques in plastics are
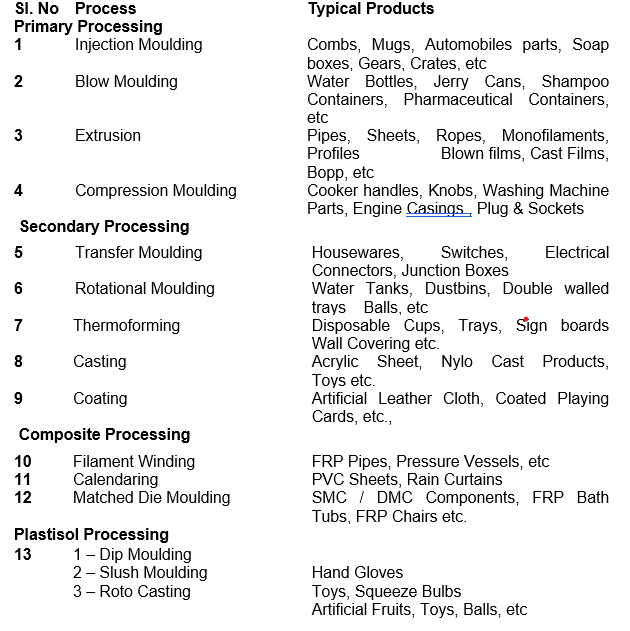


Fig: Injection molding Products
INJECTION MOULDING – Solid Wide neck, Flat Product is made like bucket, cabinets, Automobile & Industrial parts etc…. by injecting molten thermoplastic material in to a closed mould which is relatively cool
•Plasticises the material by reciprocating Screw.
•Injects the molten material to a closed mould
–via a channel system of gates and runners.
•Cools the Mould.
•Refills the material for the next cycle.
•Ejects the Product.
•Closes the Mould for further cycle.
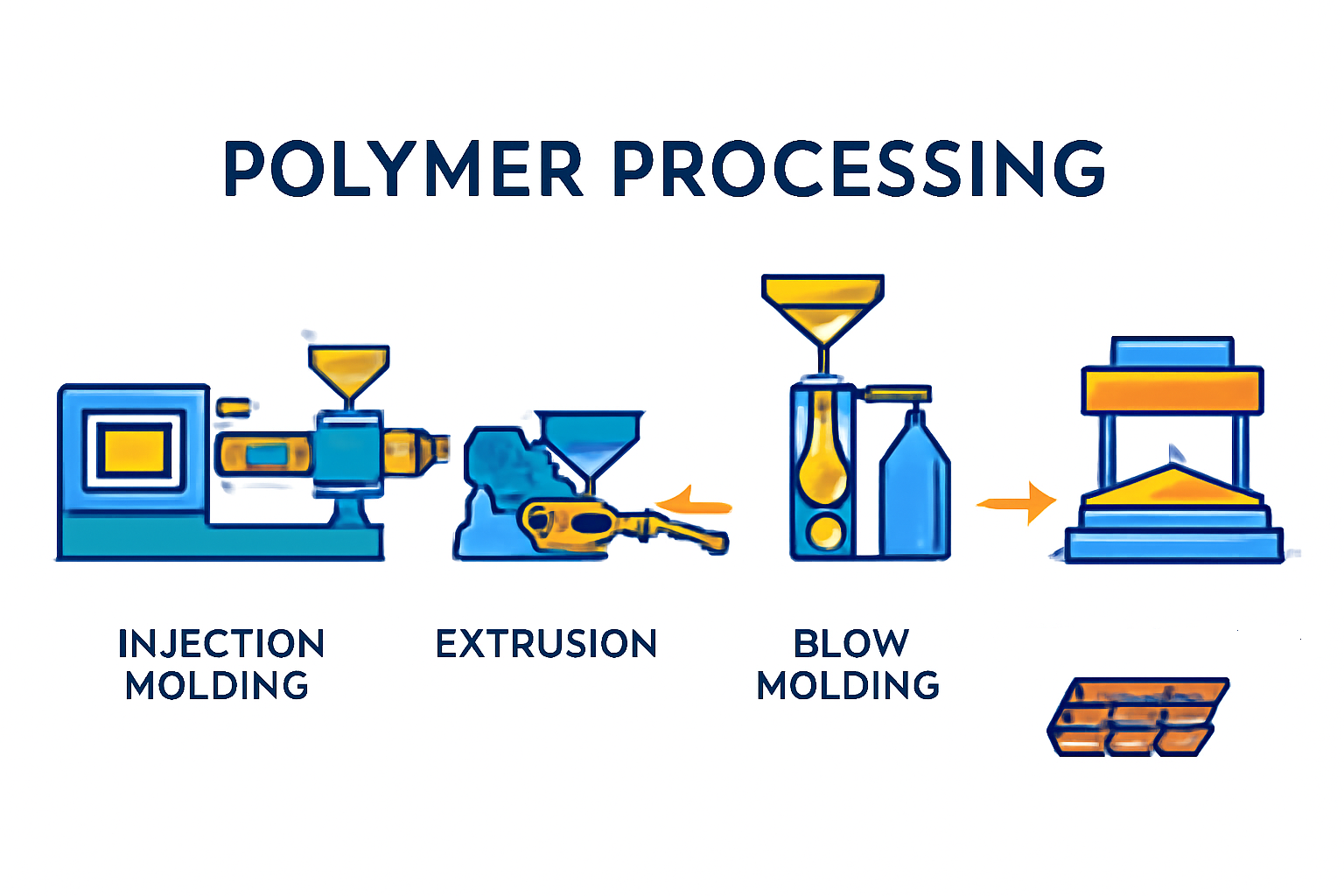
COMPRESSION MOULDING : Compression moulding is a process of moulding a material in a confined shape by applying pressure and heat.
The mould is closed with a top force or plug.
Pressure is applied to force the materials come in contact with all mould areas.
Heat and pressure are maintained until the moulding material has cured.
The process employs thermosetting resins in a partially cured stage, either in the form of granules, putty-like masses, or preforms
BLOW MOULDING PROCESS : Blow moulding is a method of fabrication in which a warm plastic (hollow tube) is placed between the two halves of a mould (Cavity) and forced to assume the shape of that mould cavity by use of pressure.
Blow moulding is used for producing bottles or other hollow objects from thermoplastic materials
ROTATIONAL MOULDING : Rotational moulding or rotomoulding is a method of moulding plasticswhich is ideal for the production of hollow articles, particularly sizeable.
It involves the slow tumbling, heating, and melting of a thermoplastic powder in a bi-axially rotating mould to produce seamless, hollow plastic parts
This process is typically used to mould hollow parts, especially those with complex and varied shapes not easily obtainable by other hollow-art processes.
THERMOFORMING The process involves heating a plastic sheet until soft and then draping it over a mould.
A vacuum is applied into the mould.
The sheet is then ejected from the mould.
In its advanced form, the vacuum forming process utilizes sophisticated pneumatic, hydraulic and heat controls thus enabling higher production speeds and more detailed vacuum formed applications
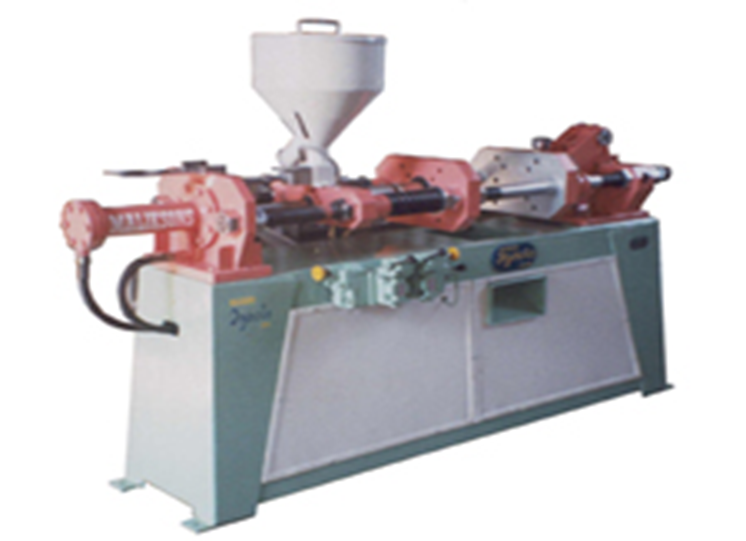
EXTRUSION PROCESS : It is a process of forming a continuous piece of plastic by forcing it through a shaping orifice with or without the presence of heat.
The opening through which the resins are forced gives the product its form, resulting in consistent thickness and gauge control.
GLUING: Gluing for assembly of plastic parts is an effective method of making permanent connections.
This method produces aesthetically clean looking joints with low weight and sufficiently strong connections.
This is a very effective joining method for heat sensitive plastics which would normally deform if welded.









Post Comment