Assessing Material Flammability Using Underwriters Laboratories Standard 94 (UL 94)
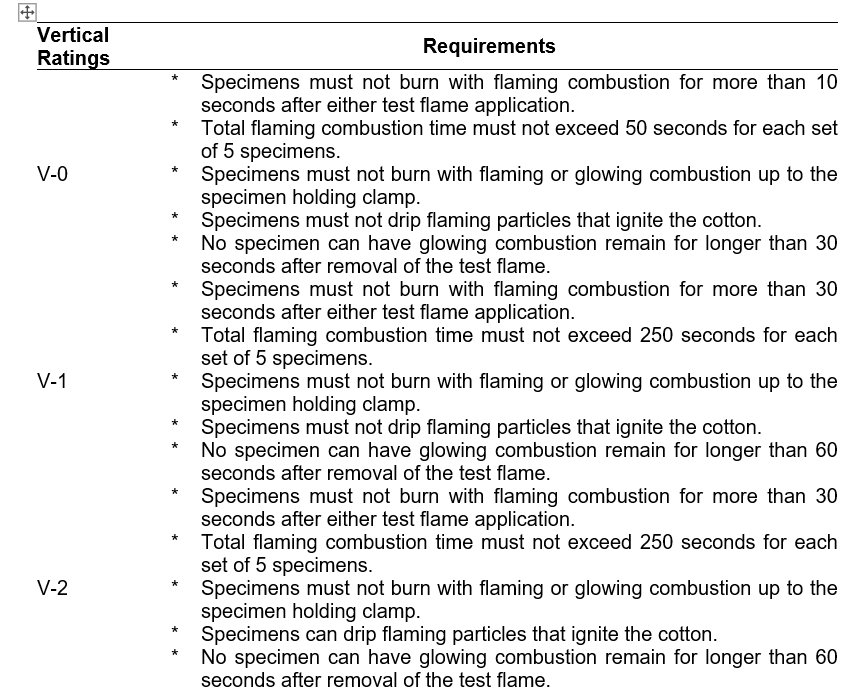
UL 94 tests measure the flammability characteristics of materials, primarily plastics, by exposing test specimens to a controlled flame or heat source. The standard classifies materials based on their burning behavior, assigning ratings such as V-0, V-1, V-2 (vertical burning), HB (horizontal burning), or 5VA/5VB (more stringent tests for enclosures).
Most plastics are carbon-based materials and will burn and give off gases and smoke when subjected to a flame. Plastics are excellent fuels but are generally classed as ordinary combustibles and fall into the same category as wood, leather and many other common materials.
All of these materials will degrade at very high temperatures into volatile and gaseous combustion products.
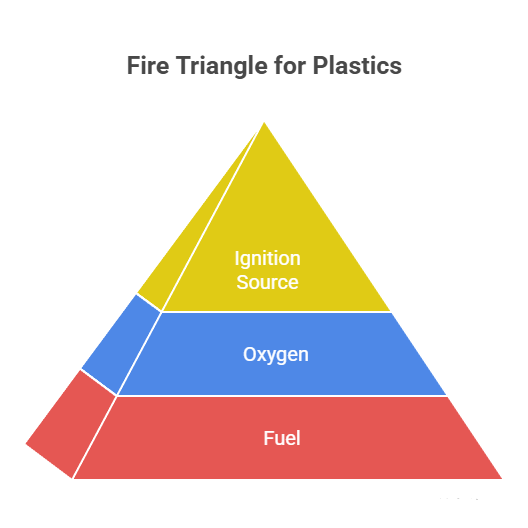
For combustion to take place three components are necessary – these form the ‘fire triangle.’ Removing any one of the components will prevent or extinguish a fire. The components are: fuel, oxygen and ignition source.

| For plastics, the actual process of combustion is very complex but broadly follows 6 separate stages: |
- Primary Thermal: The ignition source heats the bulk plastic to create a rise in temperature that depends on the product and the ignition source energy output.
- Primary Chemical: The heated plastic starts to degrade, generally through the formation of free radicals, under the influence of the ignition source. This is similar to the conventional thermal degradation of plastics discussed in earlier newsletters but is generally more rapid because of a higher energy input from the ignition source.
- Polymer Decomposition: The plastic starts to rapidly degrade into a range of lower molecular weight decomposition products. Typical products at this stage are combustible gases and liquids, charred solids and possibly smoke.
- Ignition: The combustible gases, in the presence of sufficient oxygen and the ignition source, ignite to start combustion. As noted above it is the combustible gases and liquids that burn and not the bulk material.
- Combustion: The burning gases produce combustion at or near the surface of the bulk plastic and the process can become self-sustaining if it produces sufficient energy
- Following tests are carried out for determining the flammability characteristics in Plastics
- UL 94
- Limiting Oxygen Index
- Rate of burning
- Smoke density
UNDERWRITERS LABORATORY STANDARD 94 (UL94)
Definition: UL testing is a method of classifying a material’s tendency to either extinguish or spread a flame once it has been ignited.

Significance:
- There are 12 flame classifications specified in UL 94. The classifications are used to describe materials burning characteristics after test specimens have been exposed to a specific test flame under controlled laboratory conditions.
- The classifications relate to rate of burning time to extinguish ability to resist dripping and whether or not the drips are burning.
- Six (6) of the classifications, relate to commonly used materials in enclosures, structural parts and insulators.
- According to UL, this standard has been harmonized with IEC 60707, 60695-11-10 and 60695-11-20 and ISO 9772 and 9773.
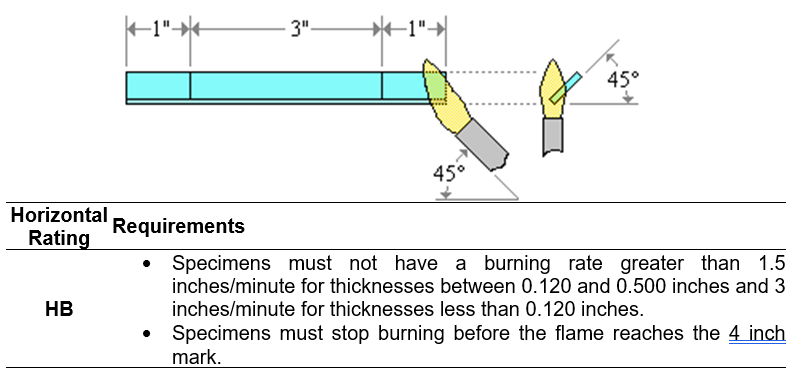
Test Method: IEC 60707, 60695-11-10 and 60695-11-20 and ISO 9772 and 9773.
Specimen Dimensions: Rectangular specimen of dimensions 125 x 15 mm (5 x ½ in) and the thickness varies but should be similar to the final product.
Equipment:
- Laboratory Fume Hood: Having an inside volume of at least 0.5 m3, is to be used when testing the specimens.
- Laboratory Burner: A laboratory type burner having a tube with a length of 100 ±10 mm and an inside diameter of 9.5±0.3 mm.
- Burner Wing Tip: A wing tip with dimensions of slit 48±1 mm length by 1.3 ± 0.05 mm in width, for the burner.
- Burner Mounting Fixture: Capable of positioning the burner at an angle of 20 degrees from the vertical axis.
- Ring Stands: Laboratory ring stands with champs or the equivalent, for horizontal or vertical positioning of the specimen and/or the wire gauze.
- Timing Devices
- Measuring Scale: Graduated in mm.
- Gas Supply: A supply of technical grade methane gas (min. 98 percent pure) with regulator and meter for uniform gas flow.
- Wire Gauze: Having approximately 20 openings per 25 mm, made with 0.43 ± 0.03 mm diameter iron wire and cut to approximately 125 mm squares.
- Conditioning Room or Chamber: Capable of being maintained at 23 ± 2oC and a relative humidity of 50 ± 5 percent. (
- HB Support Fixture: A metal support fixture for testing specimens that is not self-supporting. (Used for the test procedure in Horizontal Burning Test).
- Micrometer: Capable of being read to 0.01 mm.
- Cotton: A supply of absorbent 100 percent cotton.
- Desiccator: A desiccator containing anhydrous calcium chloride, or other drying agent, maintained at a relative humidity not exceeding 20 percent at 23 ± 2oC.
- Conditioning Oven: A full draft air-circulating oven, minimum of 5 air changes per hour, capable of being maintained at 70 ± 1oC for industrial laminates.
- Specimen Mandrel Form: Made from 12.7 ± 0.5 mm diameter rod. (Used for the test procedure in Thin Material Burning Test; VTM-0, VTM-1, VTM-2
- Tape: Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive. (Used for the test procedure in Thin Material Burning Test; VTM-0, VTM-1, VTM-2).
- Support-Gauze: A wire cloth of plain weave, low carbon, plain steel or stainless steel, approximately 215 mm long by 75 mm wide having 13 mm of its length bent to form a right angle at one end. It is to consist of 6.4 mm mesh gauze constructed of 0.88 ± 0.05 mm diameter steel wire.
- Manometer/Pressure Gage: A gage capable of measuring to 200mm of water, with increments of 5 mm.
- Flow Meter
- Test procedure:
- Horizontal Testing (HB)
- A specimen is supported in a horizontal position and is tilted at 45°.
- A flame is applied to the end of the specimen for 30 seconds or until the flame reaches the 1 inch mark.
- If the specimen continues to burn after the removal of the flame, the time for the specimen to burn between the 1 and 4 inch marks are recorded.
- If the specimen stops burning before the flame spreads to the 4 inch mark, the time of combustion and damaged length between the two marks is recorded.
- Three specimens are tested for each thickness.
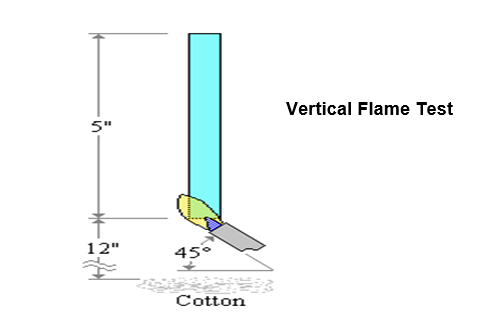
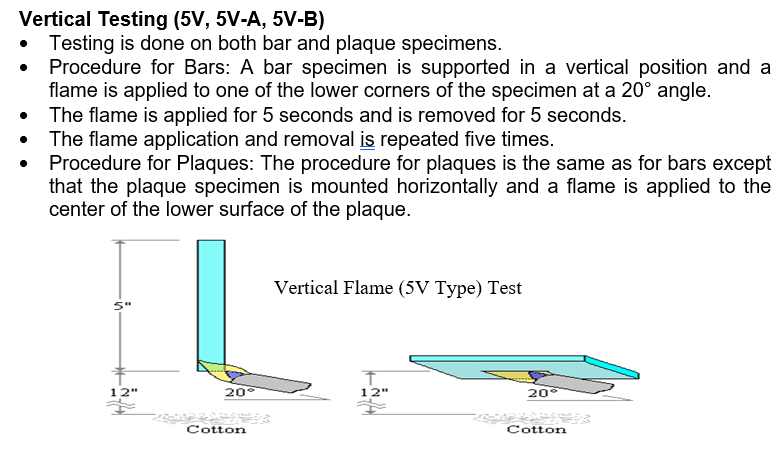
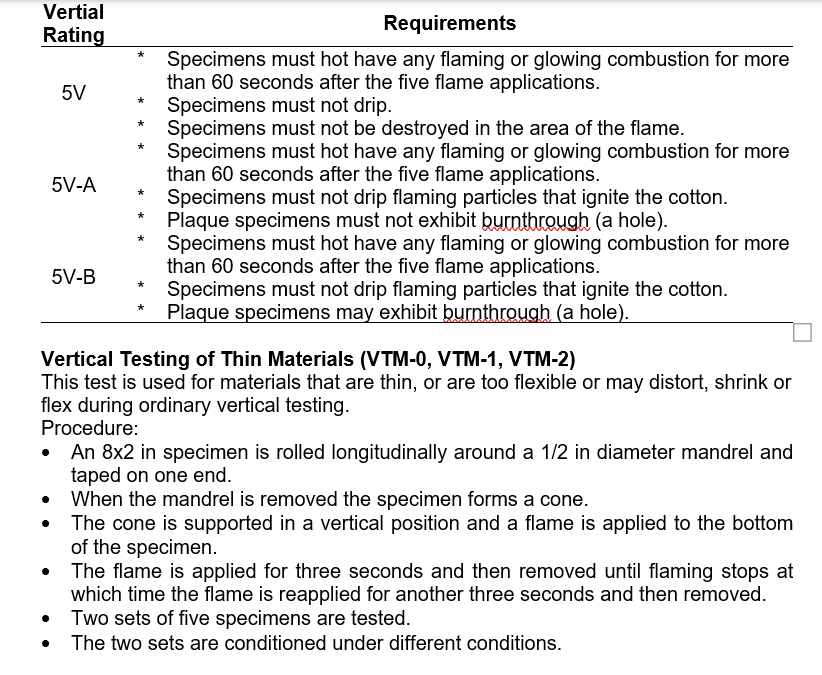
Vertical Testing (V-0, V-1, V-2)
- A specimen is supported in a vertical position and a flame is applied to the bottom of the specimen.
- The flame is applied for ten seconds and then removed until flaming stops at which time the flame is reapplied for another ten seconds and then removed.
- Two sets of five specimens are tested.
The two sets are conditioned under different conditions









Post Comment