Determination of Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) of Polymers Using ASTM D2863
LOI is defined as the minimum oxygen concentration value expressed in volume percent (in a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen) required for the continuous combustion of the material under specified testing condition.
In this article we study about standard methods- ASTM D2863, ISO 4589
The LOI is a measure of the percentage of oxygen that has to be present to support combustion of the plastic – the higher the LOI the lower the flammability.

Significance
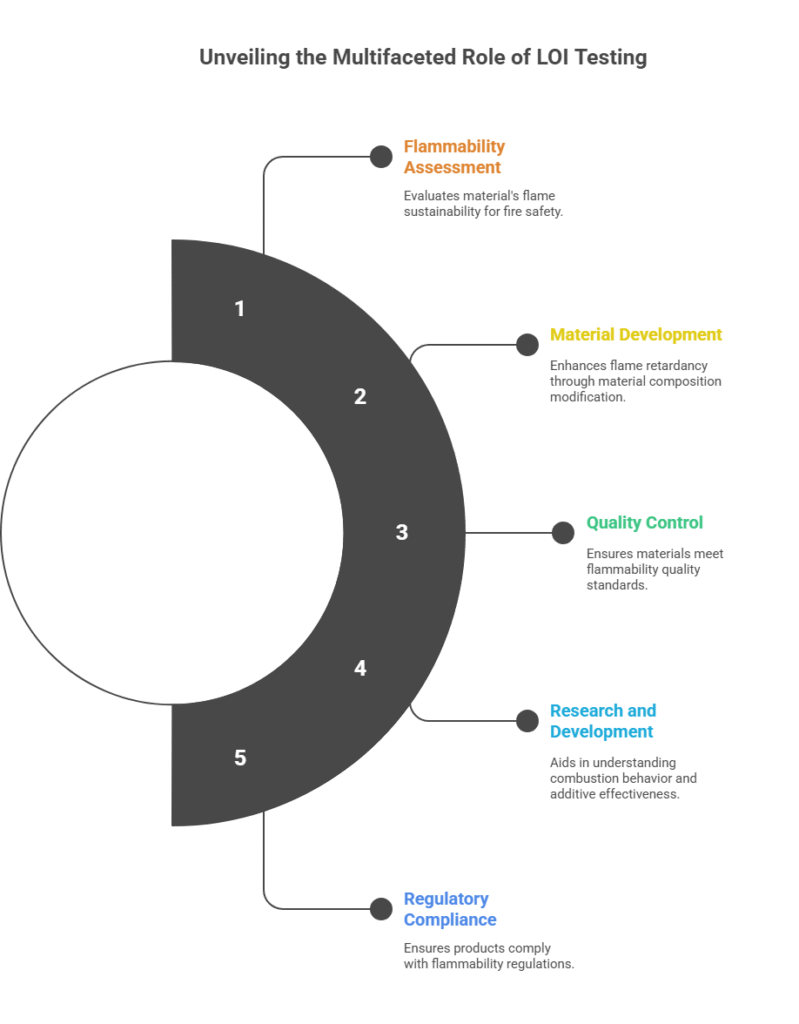
- Describes the tendency of a material to sustain a flame, is widely used as a tool to investigate the flammability of polymers.
- Measures of the minimum concentration of oxygen in flowing mixtures of oxygen and nitrogen that will just support flaming combustion of plastics.
- A high index, therefore, is indicative of a less easily ignited and less flammable material
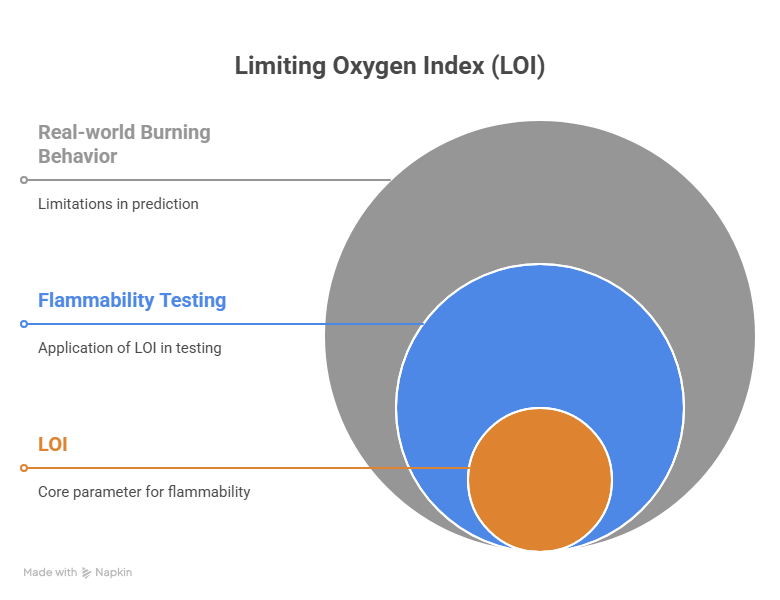
The LOI value is a basic property of the plastic but tells us nothing about how the plastic will react to burning in an open atmosphere.
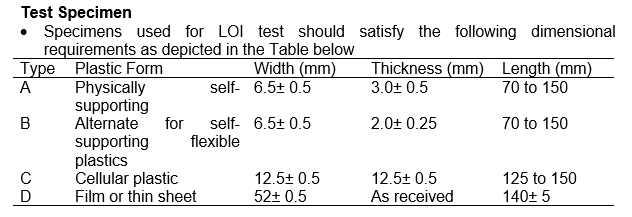
Test Method: ASTM D2863, ISO 4589
Equipment
Test apparatus used for the determination of LOI is enumerated in Fig.
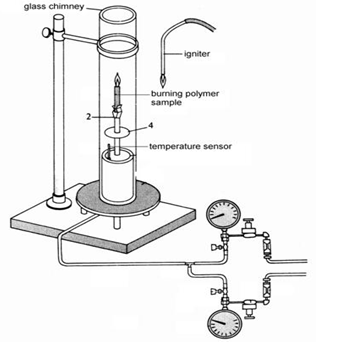
- Test Column: consisting of a heat-resistant glass tube of 75mm minimum inside diameter and 450mm minimum height. The bottom of the column or the base to which the tube is attached shall contain noncombustible material (Glass beads 3 to 5mm in diameter in a bed 80 to 100mm deep) to mix and distribute evenly the gas mixture entering at this base.
- Specimen Holder: Any small holding device that will support the specimen at its base and hold it vertically in the center of the column is acceptable.
- Gas Supply: Commercial grade (or better) oxygen and nitrogen shall be used.
- Flow Measurement and Control Devices: Suitable measurement and control devices shall be available in each line that will allow monitoring the volumetric flow of each gas into the column within 1% in the range being used.
- Ignition Source: The igniter shall be tube with a small orifice (1 to 3mm in diameter) having a hydrogen, propane, or other gas flame at the end that can be inserted into the open end of the column to ignite the test specimen. A suitable flame may be from 6 to 25mm long.
- Timer: A suitable timer capable of indicating at least 10 min and accurate at 5s shall be used.
- Soot, Fumes and Heat Removal: To ensure the removal of toxic fumes, soot, heat and other possible products, the column shall be installed in a hood or other facilities providing adequate exhaust
Test Procedure
- Calibrate the flow-measuring system using a water-sealed rotating drum meter (wet test meter) in accordance with Method D 1071 or by equivalent calibration devices.
- Clamp the specimen vertically in the approximate center of the column with the top of the specimen at least 100mm below the top of the open column.
- Select the desired initial concentration of oxygen based on the burning characteristics of the material.
- a) If the specimen burns rapidly, start at a concentration of about 18%,
- b) If the specimen goes out, select a concentration of about 25% or higher depending on the difficulty of ignition and time of burning.
- Set the flow valves so that the gas flow rate in the column shall be 4 ± 1mm/s calculated at standard temperature (0oC) and pressure (101.3 kPa) from the total flow of gas in mm3/s, divided by the area of the column in mm2.
- Allow the gas to flow for 30s to purge the system.
- Ignite the entire top of the specimen with the ignition flame so that the specimen is well lighted.
- Remove the ignition flame and start the timer.
- The concentration of oxygen is too high and must be produced if the specimen burns in accordance with one of the following criteria in table:

- Do not adjust the oxygen concentration after igniting the specimen.
- The concentration of oxygen must be raised if the flaming of the specimen extinguishes before meeting the criteria in the above table
- Perform the test at least three times by starting at a slightly different flow rate still within the 30 to 50-mm/s limits

Factors influencing:
- LOI values decreases with the increase in the test temperature
- LOI increases with the increase in the moisture in the specimen
- Incorporation of fillers & flame retardant increases the LOI value
- Increase in the thickness of the specimen increases LOI
Conclusion
The Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) is a valuable tool for assessing the flammability of materials, particularly polymers. It provides a quantitative measure of the minimum oxygen concentration required to sustain combustion under specified test conditions. While the LOI is widely used in material selection, development, and quality control, it’s important to consider its limitations and interpret the results in the context of real-world fire scenarios. Other flammability tests and considerations are necessary for a comprehensive assessment of fire risk.








Post Comment