How to Measure Rate of Burning in Plastics Using ASTM D 635
ASTM 635 Method covers a small-scale laboratory screening procedure for comparing the relative rate of burning and / or extent and time of burning of self-supporting plastics or panels and tested in the horizontal position. The flammability test evaluates the relative burning rate of self-supporting plastics, primarily for quality control, production control, and material comparisons
ASTM D635 is a small-scale laboratory test designed to assess the burning behavior of self-supporting plastic materials.
Specifically, it determines the relative burning rate, extent of burning, and burning time of plastic specimens when exposed to a small flame under controlled laboratory conditions. The test is performed with the specimen oriented horizontally.
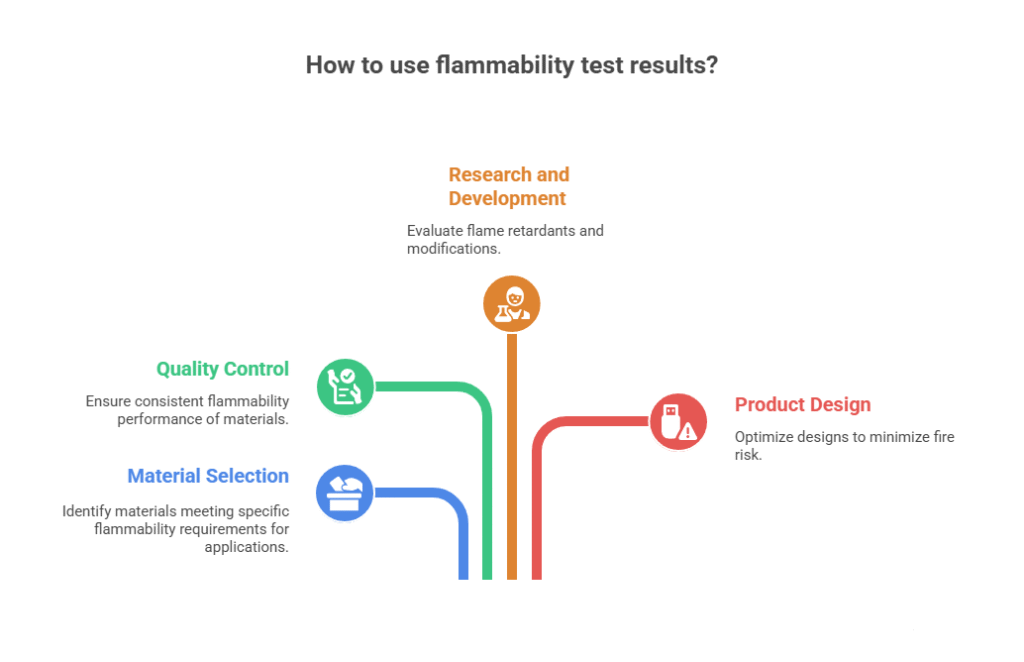
Significance:
- Compares the rate of burning and/or extent and time of burning characteristics of different materials, in controlling manufacturing processes,
- Measures the deterioration or change in these burning characteristics prior to or during use.
- It is important to note that ASTM D635 is a screening test and the results obtained should not be used to predict the fire behavior of materials under actual fire conditions.
- Other factors, such as ventilation, heat flux, and material geometry, can significantly influence the fire performance of a material.
Test Method
- ASTM D 635 Standard Test Method for Rate of Burning and / or Extent and Time of Burning of Self – Supporting Plastics in a Horizontal Position
- ASTM D 1433 Standard Test method for rate of burning of flexible thin plastic sheeting supported on a 450 incline
Specimens Dimension: 125 ± 5mm in length by 12.5 ± 0.2mm in width and of thickness of material normally supplied as per ASTM D 635
Apparatus (ASTM D 635)
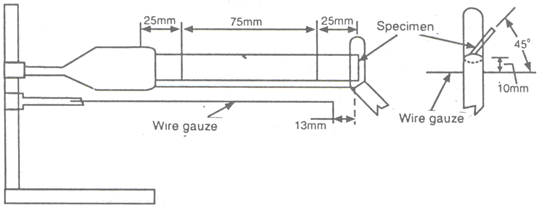
- Test Chamber: a laboratory hood, totally enclosed, with a heat-resistant glass window for observing the test.
- Ring Stand: a laboratory ring stand with two adjustable small clamps
- Laboratory Burner
- Wire Gauze: 20-mesh, 125mm square.
- Timing Device : Stop watch or other timer, with smallest division – 1 s or less.
- Pan of water.
- Scale: graduate in millimeters.
Test Procedure (ASTM D 635):
- Clamp the specimen at the end nearest the 100mm mark, in a support with its longitudinal axis horizontal and its transverse axis inclined at 45o to the horizontal.
- Under the test specimen clamp a screen of wire gauze (approximately 125 by 125mm) in a horizontal position 10mm below the edge of the specimen and with the free end of the specimen even with the edge of the gauze
- A pan of water should be placed on the floor of the hood in position to catch any burning particles that may drop during the test.
- Place the burner remote from the specimen, ignite and adjust it to produce a blue flame 20mm high.
- Place the burner so that the flame contacts the end of the test specimen
- Starting the stop watch simultaneously apply the flame for 30 secs. If the specimen warps, melts or shrinks away from the flame, move the flame to keep it in contact with the specimen.
- Excessive distortion of the specimen during the test may invalidate the results.
- Remove the burner at 30s or when the flame front reaches the 25mm mark, whichever comes first and place the burner at least 450mm from the specimen and close the hood.
- Record the time, in seconds, on the watch when the flame front reaches the 25mm mark, as burning time t1.
- If the burning has not reached the 100mm mark, measure the unburned length to the nearest 1mm along the lower edge of specimen from the mark.
- The extent of burning is defined as 100mm minus the unburned length in the same units.
- If the specimen has burned to or beyond the 100mm mark, calculate the burning rate as 450/(t-t1) (cm/min).
- Repeat the procedure until three specimens have burned to or beyond the 100mm mark, or ten specimens have been tested.
- If only one of 10 specimens tested burns to the 100mm mark or beyond, repeat the procedure with ten additional specimens.
Calculation:
Average Time of Burning (ATB):
ATB = [Σ(t – 30s)]/number of specimens
rounded (after averaging) to the nearest multiple of 5s; that is, less than 5 s, would be reported if burning or glowing continued less than 3s after removal of flame. In one case is an ATB of zero to be recorded.
Average Extent of Burning (AEB):
AEB, mm = [Σ(100mm – unburned length)]/number of specimen Rounded (after averaging) to the nearest 5mm; extent of burning less than 3mm, report as less than 5mm, in no case reporting zero. Extent of burning of a single specimen that burns to the mark is counted as 100mm.
Conclusion : ASTM D635 is a valuable tool for evaluating the flammability characteristics of self-supporting plastic materials. By following the specified procedures and carefully interpreting the results, users can make informed decisions about material selection and product design to minimize the risk of fire. However, it is crucial to remember that this test is a small-scale screening method and the results should not be used to predict the fire behavior of materials under actual fire conditions.
For All Type of polymer Testing Subscribe our podcast cast channel :
https://www.youtube.com/@polymertesting99









Post Comment