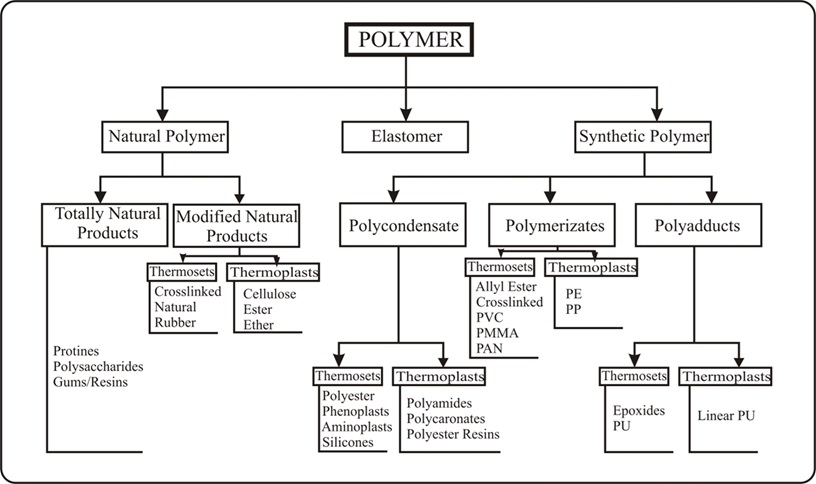
Polymer Fundamental: Basics of Polymer

Polymers are a large class of materials consisting of many small molecules (called monomers) that can be linked together to form long chains, thus they are known as macromolecules
“The chemical approach assumed that polymer (poly- many; mer-unit or parts) is a high molecular weight compound, formed by the combination of a large number of one or more types of molecule of low molecular weight”.
Polymerization: “Polymers are giant molecules, called macromolecules, which are built up by the linking together of a large number of small molecules, called monomers and the reaction by which monomers combine to form polymers is known as polymerization”
Degree of Polymerization (DP): “The numbers of repeating unit present in it call degree of polymerization (DP)”.
Addition Polymerization: When molecules just add on to form the polymer, the process is called ‘addition polymerization’
The molecular Weight is just multiple of the molecular weight of the monomer.
Polymer Material Properties Depends on
1.Degree of Polymerization
2.Molecular Weight of the Polymer
3.Molecular Weight Distribution
4.Glass Transition Temperature
5.Percentage of Crystallinity
6.Percentage of Amorphous Content in the Polymer
7.Structure and Distribution of Chain Branching
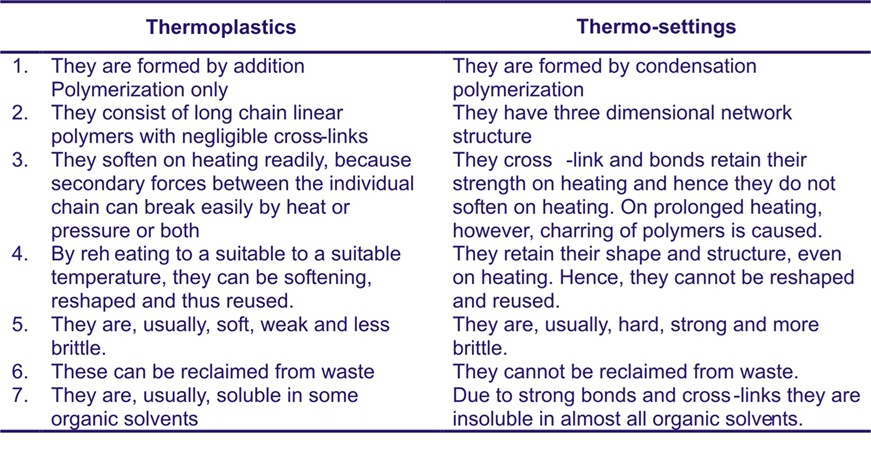
Thermoplastics Polymers : Thermoplastics are resins that repeatedly soften when heated and harden when cooled
Thermosetting Polymers :Thermosets are resins that undergo chemical changes during processing to become permanently insoluble and infusible due to they formed three-dimensional cross linked network structure when heat is applied.
Difference Between Thermoplastics and Thermosetting Polymers
Polymer Structure and Morphology: In additions to size of the molecules and their distribution, the shapes or structure, of individual polymer molecules also play an important role in determining the properties and process-ability of plastics.
Because of the geometry, or morphology, of those molecules some can come closer together than other. These are defined as crystalline, all other are as amorphous. Morphology influences such properties as mechanical and thermal, swelling and solubility, specific gravity and chemical and gravity properties.
This behavior of morphology basically occurs with thermoplastics, not thermosetting. When thermosetting are processed, their individual chain segments are strongly together during a chemical reaction that is irreversible.









Post Comment